Services
Our business is people. We build relationships with each of our clients in order to provide the expertise you need to achieve your goals in the following services:
-
Develop and implement the components of a Records Information Management (RIM) Program includes the following aspects:
- Initiate a preliminary assessment of organization’s legal and business environments
- Conduct business functions and activities analysis to map business processes, transactions and records creation requirements
- Conduct records assessment and records inventory (paper & electronic)
- Capture and document functional requirement and workflow models
- Determine recordkeeping requirements and define metadata standards requirements
- Producing a Records Policy to include freedom of information and protection of privacy and email management
- Producing instructions and training materials for managing paper/electronic records
- Establish Business Classification Scheme based on business function
- Producing a Records Retention Schedule to comply with legislation, industry regulations and ISO Standards
- Producing a Records Procedures (legal hold, storing, retrieval, archival, destruction)
- Design an Electronic Records Management System (ERMS) to include processes, tools and systems required to implement the program
- Facilitating electronic record systems assessment and identify user specifications in order to assist in the selection process for a software vendor
- Auditing records policy application across your company and design a Vital Records Program
- Measuring current records management practices against national and international standards and making recommendations for improvement
- Change management strategies and communication plan
- Support Risk Management and Business Continuity Planning
- Awareness and education programs for Records Information Management Program
- Conducting an annual records clean-up day for paper and electronic records
- Planning and conducting the implementation process and the post-implementation review
- Staff Training and Workshops on Records Information Management Program
- Carry out review and issuing reports to ensure continued effectiveness of the Records Information Management (RIM) program
-
Develop and Implement Document Control Plan for any EPCM Projects (engineering-procurement-construction & management).
A document control plan is basically a guide that explains the management procedure of documents (paper & electronic) during the project lifecycle. This plan is established for ensuring proper documentation in a project, and contains the following components:
- Construction Work Package Process
- Change Control Process
- Document Control Procedures (create, review, approval, distribute)
- Document Coding System
- Document Control Turnover
- Document Identification Conventions
- Document Audit Process
- Document security and control access
- Engineering Work Package Process
- Implementing Electronic Document Management System
- Project filing Structure
- Project forms & template
- Prepare training materials and deliver training sessions
- Quality Management Plan
- Technical Document Policy
-
Design and Implement the Information Governance Program including:
- Information Governance Gap Assessment
- Information Governance Reference Model (IGRM)
- Information Governance Program Strategy Design
- Privacy
- Data Protection
- Discovery & Legal Holds
- Records and Information Management
-
Project Management
Managing and guiding projects step-by-step through every detail, always mindful of the big picture as we help clients move from ideation to completion. Below are five (5) project management phases:
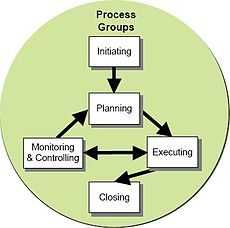
- Initiation
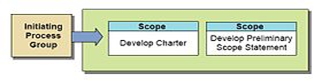
The initiating processes determine the nature and scope of the project. If this stage is not performed well, it is unlikely that the project will be successful in meeting the business’ needs. The key project controls needed here are an understanding of the business environment and making sure that all necessary controls are incorporated into the project. Any deficiencies should be reported and a recommendation should be made to fix them.
The initiating stage should include a plan that encompasses the following areas:- analyzing the business needs/requirements in measurable goals;
- reviewing of the current operations;
- financial analysis of the costs and benefits including a budget;
- stakeholder analysis, including users, and support personnel for the project;
- project charter including costs, tasks, deliverables, and schedules.
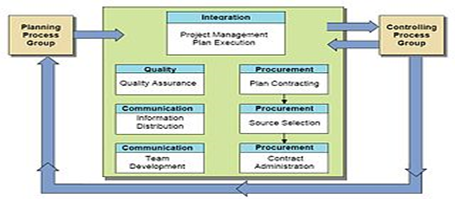
- Planning

After the initiation stage, the project is planned to an appropriate level of detail. The main purpose is to plan time, cost and resources adequately to estimate the work needed and to effectively manage risk during project execution. As with the Initiation process group, a failure to adequately plan greatly reduces the project's chances of successfully accomplishing its goals.
Project planning generally consists of:- determining how to plan;
- developing the scope statement;
- selecting the planning team;
- identifying deliverables and creating the work breakdown structure;
- identifying the activities needed to complete those deliverables and networking the activities in their logical sequence;
- estimating the resource requirements for the activities;
- estimating time and cost for activities;
- developing the schedule;
- developing the budget;
- risk planning;
- gaining formal approval to begin work.
For new product development projects, conceptual design of the operation of the final product may be performed concurrent with the project planning activities, and may help to inform the planning team when identifying deliverables and planning activities. - Execution
The execution/implementation phase ensures that the project management plan’s deliverables are executed accordingly. This phase involves proper allocation, co-ordination and management of human resources and any other resources such as material and budgets.
The output of this phase is the project deliverables. - Monitoring and Controlling
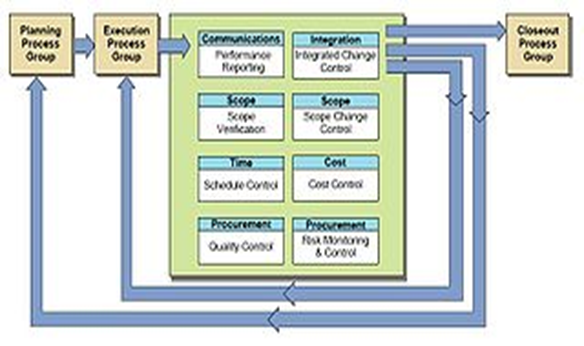
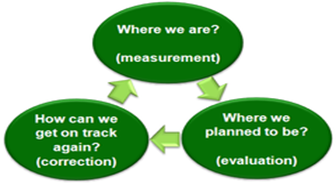
Monitoring and controlling consists of those processes performed to observe project execution so that potential problems can be identified in a timely manner and corrective action can be taken, when necessary, to control the execution of the project. The key benefit is that project performance is observed and measured regularly to identify variances from the project management plan.
Monitoring and controlling includes:- Measuring the ongoing project activities ('where we are');
- Monitoring the project variables (cost, effort, scope, etc.) against the project management plan and the project performance baseline (where we should be);
- Identify corrective actions to address issues and risks properly (How can we get on track again);
- Influencing the factors that could circumvent integrated change control so only approved changes are implemented.
- Closing
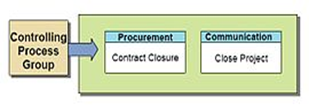
Closing includes the formal acceptance of the project and the ending thereof. Administrative activities include the archiving of the files and documenting lessons learned.
This phase consists of:- Contract closure: Complete and settle each contract (including the resolution of any open items) and close each contract applicable to the project or project phase.
- Project close: Finalize all activities across all of the process groups to formally close the project or a project phase
- Initiation